画像をダウンロード yield strength definition in material science 252492-Yield strength definition in material science
Whether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirementYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isYield strength refers to an indication of maximum stress that can be developed in a material without causing plastic deformation It is the stress at which a material exhibits a specified permanent deformation and is a practical approximation of the elastic limit In engineering structural design, yield strength is very important

What Is Yield Strength Materials Handling Definition
Yield strength definition in material science
Yield strength definition in material science-The yield strength is the point at which elastic deformation gives way to plastic deformation Deformation in the plastic range is nonlinear, and is described by the stressstrain curve This response produces the observed properties of scratch and indentation hardness, as described and measured in materials scienceCold and Hot Working Review of Materials Plastic deformation which is carried out in a temperature region and over a time interval such that the strain hardening is not relieved is called cold workConsiderable knowledge on the structure of the coldworked state has been obtained In the early stages of plastic deformation, slip is essentially on primary glide planes and the dislocations form


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers
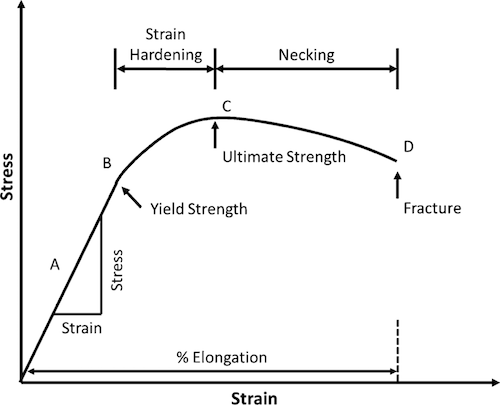
Plastic zone the zone where a material will not return to its orginal shape for a given amount of stress;Breaking point the object fails and breaks;The opposite reaction occurs upon heating
Plastic zone the zone where a material will not return to its orginal shape for a given amount of stress;Steel yield strength is the amount of stress a piece of steel must undergo in order to permanently deform A metal that has a high yield strength can withstand high stress without permanent deformation The yield strength of a bar of material is the maximum stress that can be applied along its axisA measure of a materials resistance to localized plastic deformation Term Yield Strength Definition indicative of the stress at which plastic deformation begins Term Eutectic reaction Definition upon cooling, liquid phase is transformed into its solid state a (alpha) and b (beta) phases at the temperature TE;
Strength, ductility and toughness are three very important, closely related material properties The yield and ultimate strengths tell us how much stress a mStrength, ductility and toughness are three very important, closely related material properties The yield and ultimate strengths tell us how much stress a mYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed
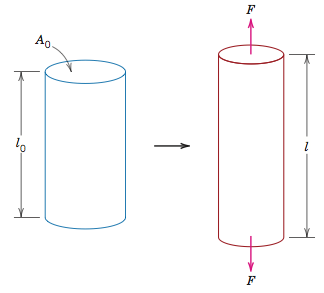


Tensile Compressive Shear And Torsional Stress Matse 81 Materials In Today S World



What Is Yield Strength Materials Handling Definition
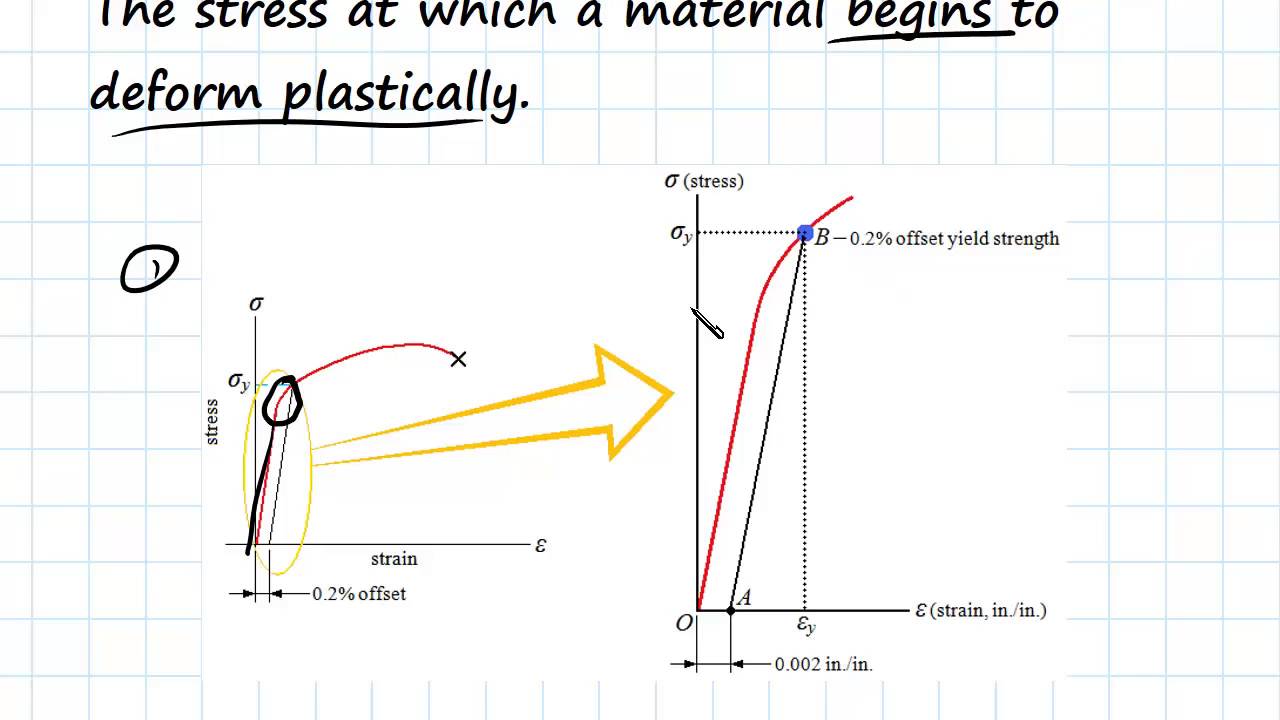
Mathematically, yield strength (in materials that do not exhibit a welldefined yield point) equals the stress that produces a specific amount of plastic deformation, usually taken as 02 percent of the unstressed length In economics, yield is defined as the amount of profit or loss recognized on a company's investmentsYield strength the amount of stress necessary to produce a specific amount of permanent deformation ;Yield strength is the stress at which a material has undergone some arbitrarily chosen amount of permanent deformation, often 02 percent A few materials start to yield, or flow plastically, at a fairly welldefined stress (upper yield point) that falls rapidly



Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers
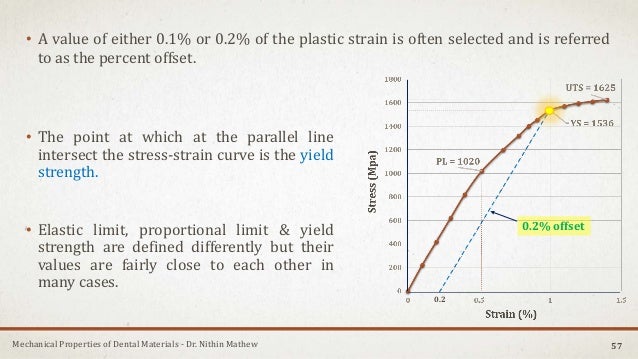
Strength of materials, also called mechanics of materials is a subject which deals with the behavior of solid objects subjected to Stress and Strain The study of strength of materials often refers to various methods of calculating the stresses anYield strength is defined as the stress at which the material exhibits a specified limiting deviation from the proportionality of stress to strain It is the amount of stress required to produce a predetermined amount of permanent strain, usually 01 or 02%, which is called the "percent offset"The tensile strength is on the basis of thread connection strength and includes yield strength, rupture strength, and slippage strength Once the casing has been run in the well, it is no longer taken out;



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University


What Is The Difference Between The Hardness Toughness Resilience And Stiffness Of Materials Quora
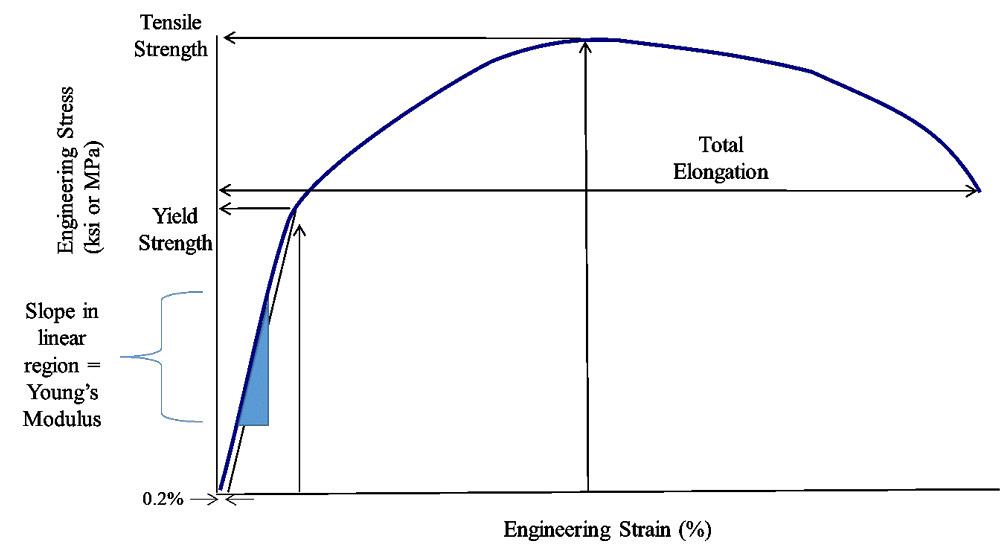
Yield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?The yield strength is the maximum force that a material can withstand without taking permanent damage Unless an application is only made to be used once, the maximum force that a material can be used for is determined by the yield strength For engineering applications of "strengthlimited design," engineers need to know the yield strengthYield strength can be explained, in engineering and materials science, as the stress at which a material begins to plastically deform Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Yield Stress Of A Material Simple Explanation Civildigital
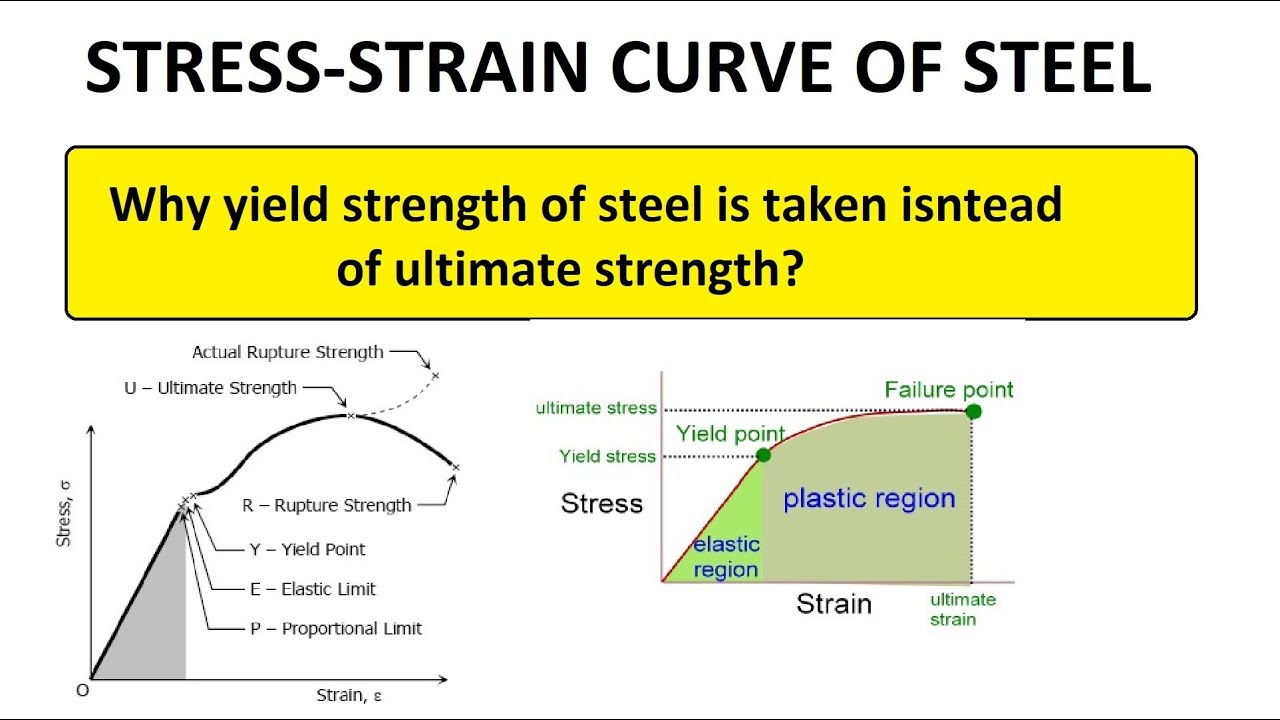
Thus the tensile strength of the casing is calculated on the basis of the ultimate tensile strength of the materialThe point at which the material transforms from elastic to plastic is known as the yield point The magnitude of the stress at which the transition from elastic to plastic occurs is known as the yield strength Yield strength is a constant that represents the maximum limit of elastic behaviourUltimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removedA most important calculation in the design of warehouses (both as buildings and as internal structures), yield strength or yield point of a material is defined in engineering and materials science as the stress at which a material begins to deform plasticallyBreaking point the object fails and breaks;
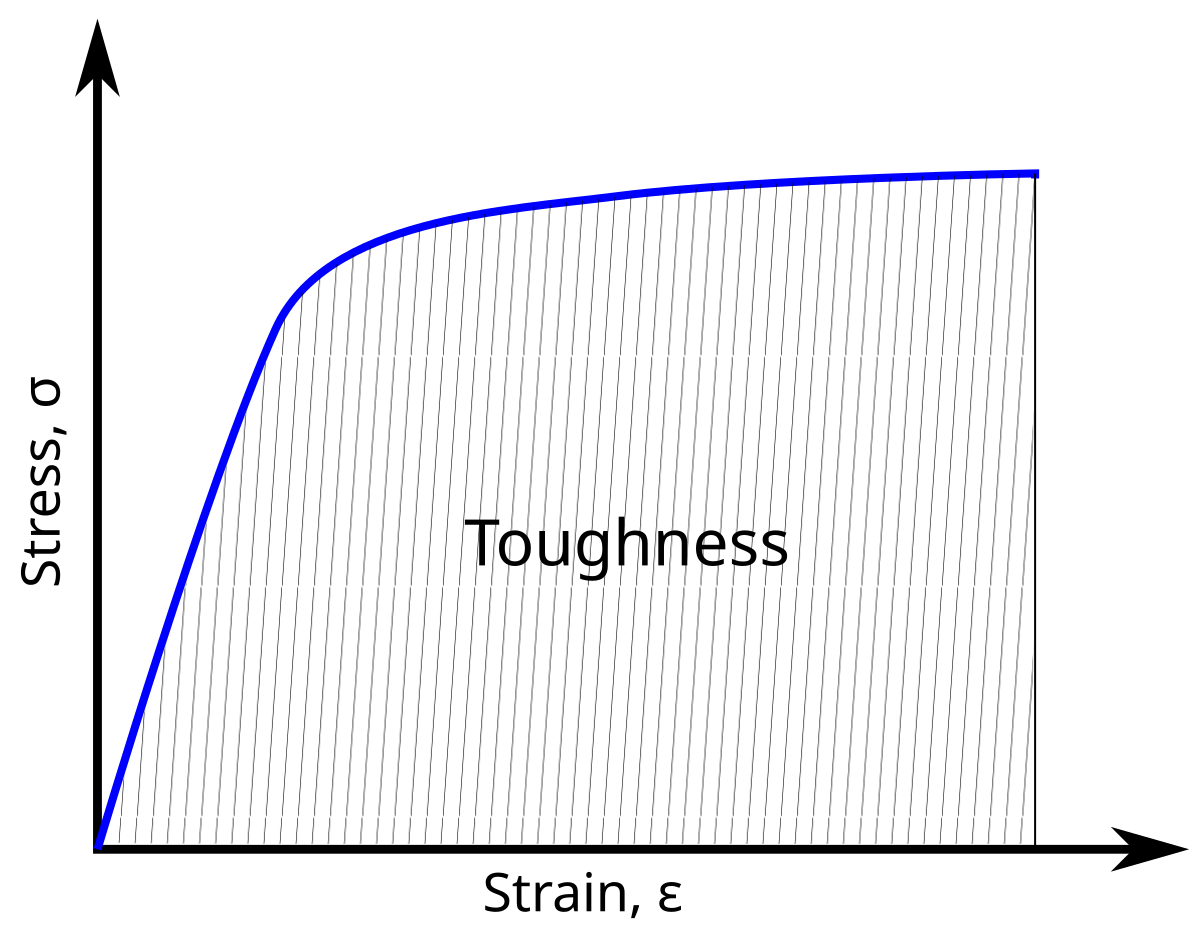


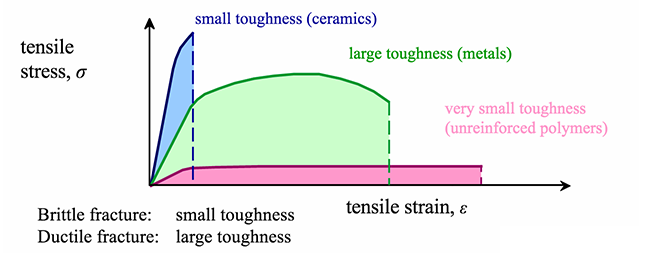
Toughness Wikipedia



Tensile Compressive Shear And Torsional Stress Matse 81 Materials In Today S World
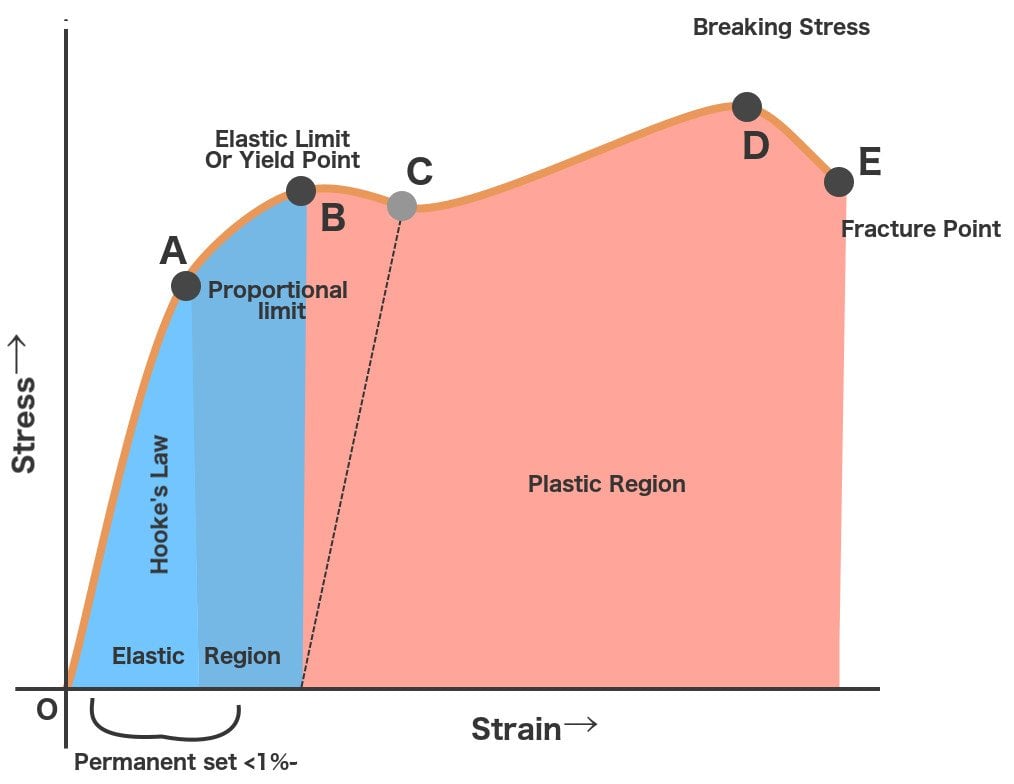
For the evaluation of strength properties, upper and lower yield points, as well as breaking strength or tear strength are determined in addition to the tensile strength Yield point is generally used to describe the stress at the transition from elastic to plastic deformation It is the generic term for elastic limit, upper and lower yield strength (tensile test), compressive yield strength (compression test), flexural yield strength (flexure test) or torsional yield strength (torsion test)Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation beginsDuctility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (eg into wire) In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stress before failure Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing, defining a material's suitability for certain manufacturing



Work Hardening Wikipedia
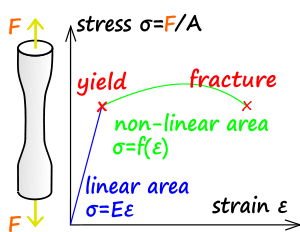


Strength Of Materials Wikipedia
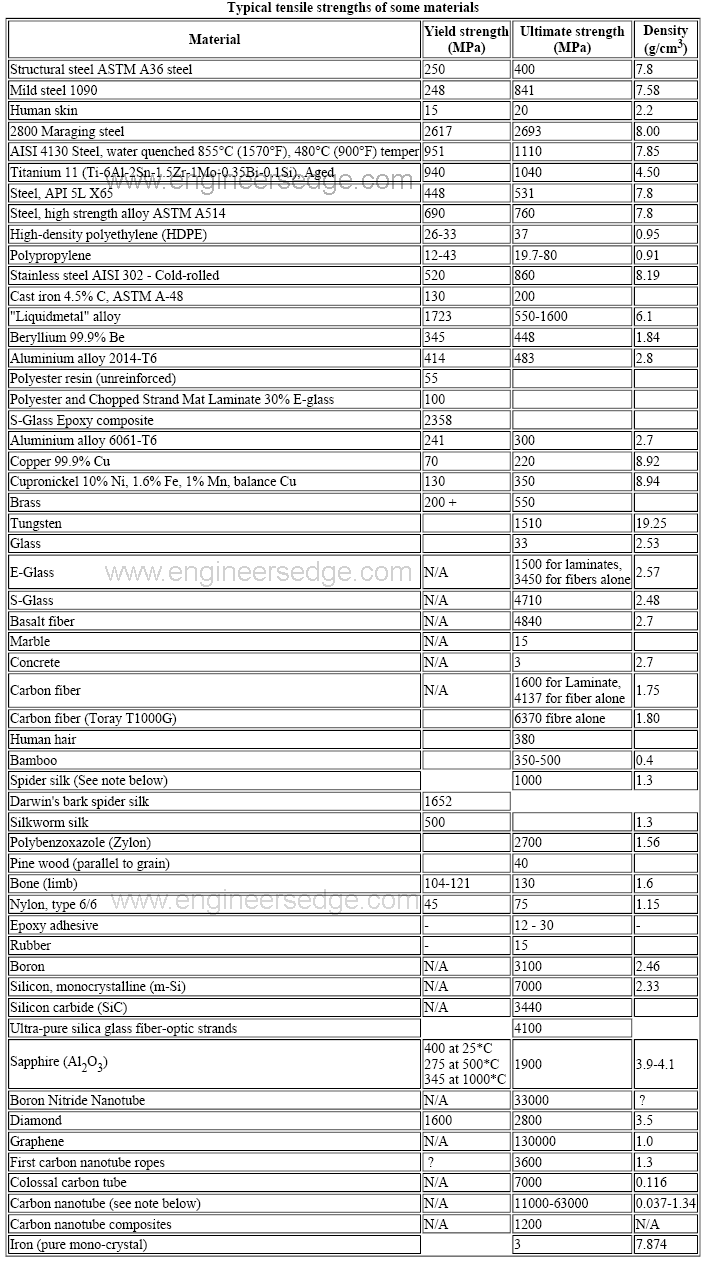
The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior Ductile materials like iron boast higher yield strength values than plastics, such as polyethylene Stresses so severe can cause permanent deformationsThe yield strength is defined as the level of stress that produces a specific amount of permanent set This means that by the time the yield strength is reached, the base material has already yielded (undergone permanent set) by definition The 02% offset yield strength (02% OYS, 02% proof stress, R P02, R P0,2) is defined as the amount ofYield strength refers to an indication of maximum stress that can be developed in a material without causing plastic deformation It is the stress at which a material exhibits a specified permanent deformation and is a practical approximation of the elastic limit In engineering structural design, yield strength is very important



Materials Science



Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets
The yield strength is defined as the level of stress that produces a specific amount of permanent set This means that by the time the yield strength is reached, the base material has already yielded (undergone permanent set) by definition The 02% offset yield strength (02% OYS, 02% proof stress, R P02, R P0,2) is defined as the amount ofYield strength The stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation This is not a sharply defined point Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstandAJ Dart, CM Dart, in Comprehensive Biomaterials, 11 Tensile Strength Tensile strength is defined by the US Pharmacopeia (USP) as the weight necessary to break a suture divided by the crosssectional area of the suture 2–4 The relationship between the weight necessary to break a suture and the suture's diameter is not linear 5 Tensile strength can be measured using either
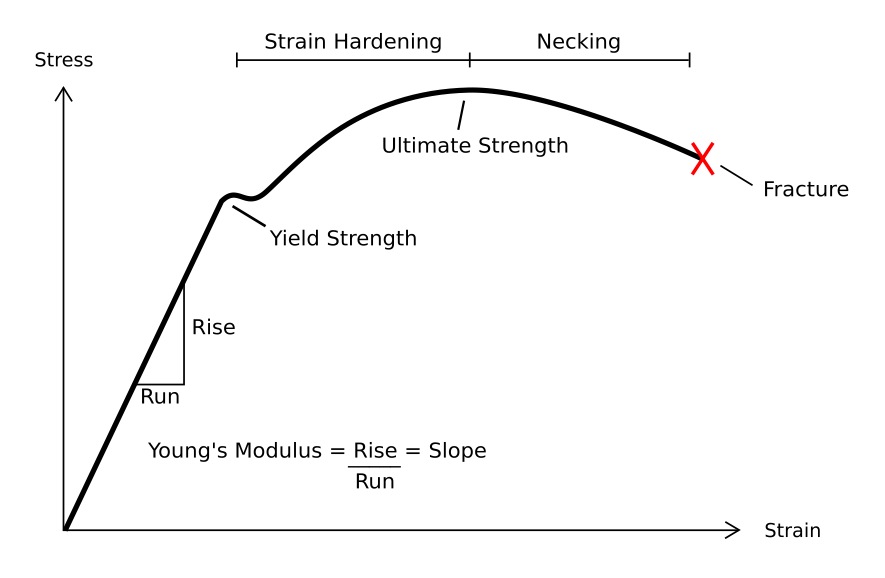


Resilience Materials Science Wikipedia


What Is The Basic Difference Between Yield Strength And Ultimate Strength For Any Elastic Material Quora
Before the fatigue cycle commences, ie at zero applied stress, the material at the weld toe is already at the tensile yield strength, Figure 711(a) As the fatigue cycle commences, further tensile stresses are applied which causes the stress at the weld toe to increase owing to work hardening, until the maximum stress in the cycle is reachedYield Strength Strength ( Mechanics ) of Materials Strength / Mechanics of Materials A number of terms have been defined for the purpose of identifying the stress at which plastic deformation begins The value most commonly used for this purpose is the yield strength The yield strength is defined as the stress at which a predetermined amount of permanent deformation occursYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed
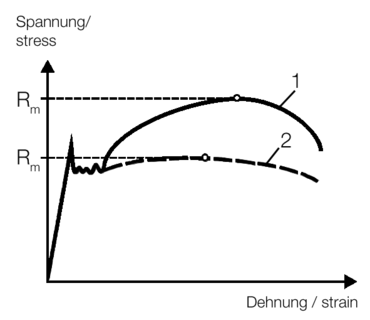


Tensile Strength Definition Of The Material Characteristic Value Zwickroell
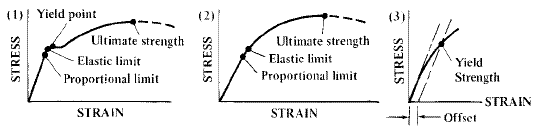


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
The yield strength is defined as the level of stress that produces a specific amount of permanent set This means that by the time the yield strength is reached, the base material has already yielded (undergone permanent set) by definition The 02% offset yield strength (02% OYS, 02% proof stress, R P02, R P0,2) is defined as the amount ofYield point the transition point between elastic and plastic deformation ;Yield point, a quantity called yield strength is substituted Yield strength is the stress at which a material has undergone some arbitrarily chosen amount of permanent deformation, often 02 percent A few materials start to yield, or flow plastically, at a fairly welldefined stress (upper yield point) that falls rapidly Read More;


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf



Resilience Resilient Material
Noun ( Mechanical engineering Materials) The yield strength of a bar of material is the maximum stress that can be applied along its axis before it begins to change shape Steel yield strength is the amount of stress a piece of steel must undergo in order to permanently deform A metal that has a high yield strength can withstand high stress without permanent deformationYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf
Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isDefinition Yield Strength Definition What is Yield Strength?Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Point at which material exceeds the elastic limit and will not return to its origin shape or length if the stress is removed This value is determined by evaluating a stressstrain diagram produced during a tensile strength test



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets
Yield point the transition point between elastic and plastic deformation ;Yield strength the amount of stress necessary to produce a specific amount of permanent deformation ;For metallic materials with a pronounced yield point the maximum tensile force is defined as the highest reached force after the upper yield strengthThe maximum tensile force after exceeding the yield strength can also lie below the yield point for weakly workhardened materials, therefore the tensile strength in this case is lower than the value for the upper yield strength



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
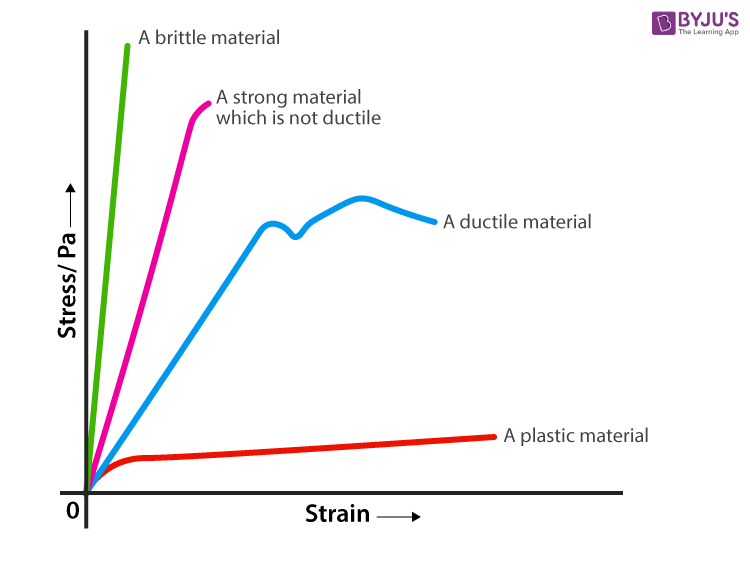
1 Introduction The high strength steel (HSS) with a nominal yield stress not less than 460 N/mm 2 has been increasingly used in engineering structures, especially in highrise buildings, spatial structures and bridges In practical engineering, most critical steel members are generally working under the multiple and complex stress states, such as the beamcolumn connectionsYield strength is the stress at which a material has undergone some arbitrarily chosen amount of permanent deformation, often 02 percent A few materials start to yield, or flow plastically, at a fairly welldefined stress (upper yield point) that falls rapidly to a lower steady value (lower yield point) as deformation continues Any increase in the stress beyond the yield point causes greater permanent deformation and eventually fractureThe magnitude of the stress at which the transition from elastic to plastic occurs is known as the yield strength Yield strength is a constant that represents the maximum limit of elastic behaviour Ductile materials like metals have higher yield strength values than plastics The stressstrain graph of different materials are given below The yield strength of steel and various metals are given in the table below


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Tensile Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
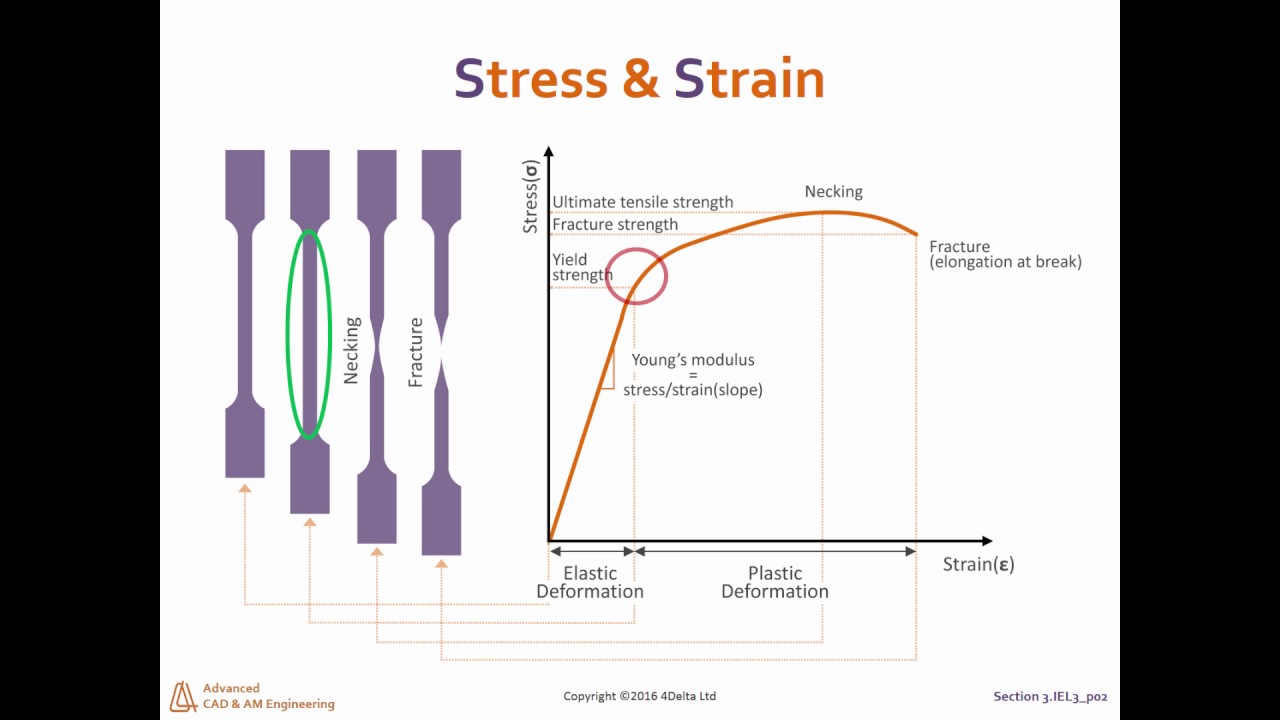
The yield point tells engineers the yield strength and yield stress The yield strength is the maximum force that a material can withstand without taking permanent damage Unless an application is only made to be used once, the maximum force that a material can be used for is determined by the yield strengthIn practice, it is difficult to identify the exact point at which a material moves from the elastic region to the plastic region As shown in the figure below, a parallel line offset by 0002 strain is drawn Where that line intercepts the stressstrain curve is identified as the yield strength The yield strength is equal to the stress atMaterials science Materials science Steel While the goal of the aluminum and plastics industries is to achieve vehicle weight reductions by substituting their products for steel components, the goal of the steel industry is to counter such inroads with such innovative developments as highstrength, but inexpensive, "microalloyed" steels that achieve weight savings by thickness reductions


Yield Stress Yield Strenght Youtube


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation
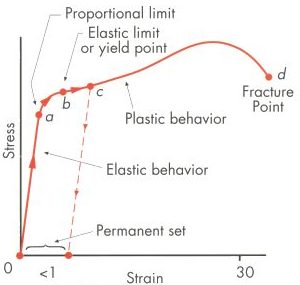
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and111 Given stressstrain curves for ductile and brittle material, IDENTIFY the following specific points on a stressstrain curve a Proportional limit b Yield point c Ultimate strength d Fracture point 112 Given a stressstrain curve, IDENTIFY whether the type of material represented is ductile or brittle


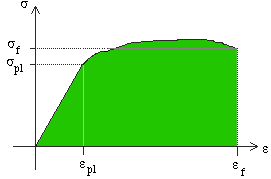
Resiliency And Toughness Matse 81 Materials In Today S World
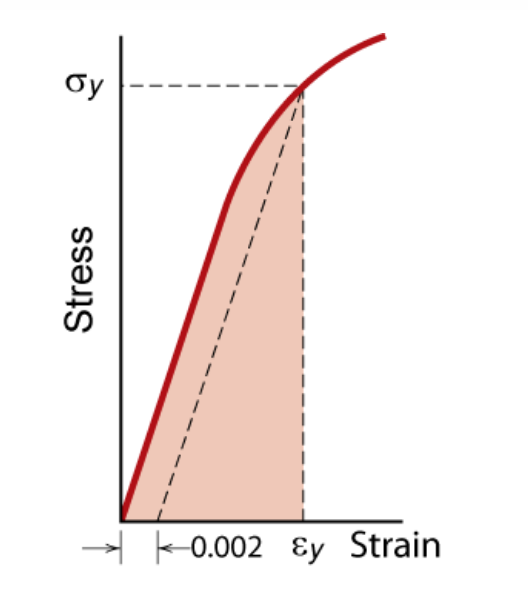


Resiliency And Toughness Matse 81 Materials In Today S World



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia



Mechanical Properties Of Dental Materials
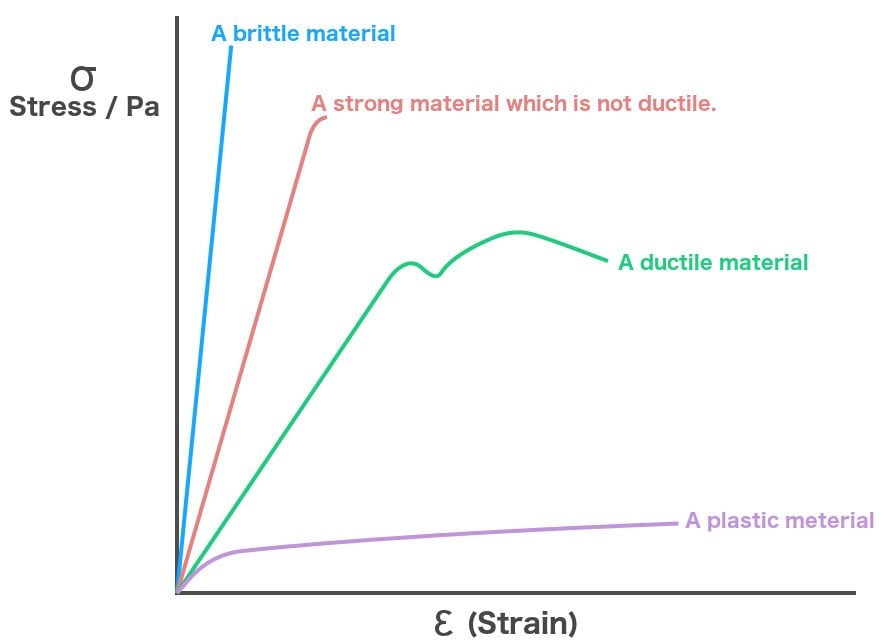


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation



Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
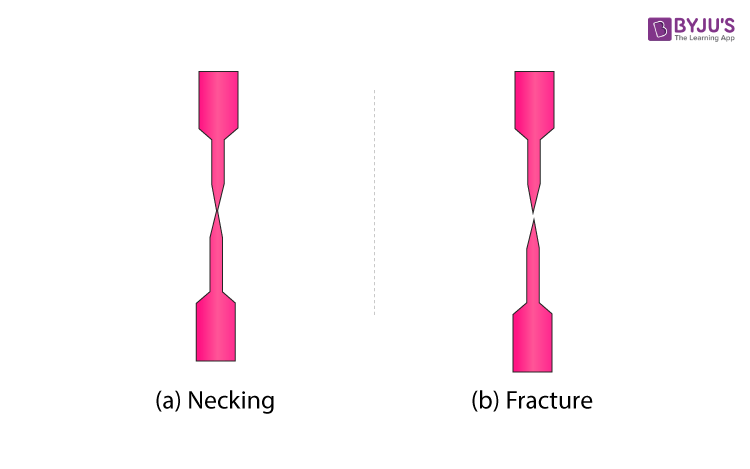


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


What Is A Compressive Strength Definition From Corrosionpedia



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Definition Of Mos
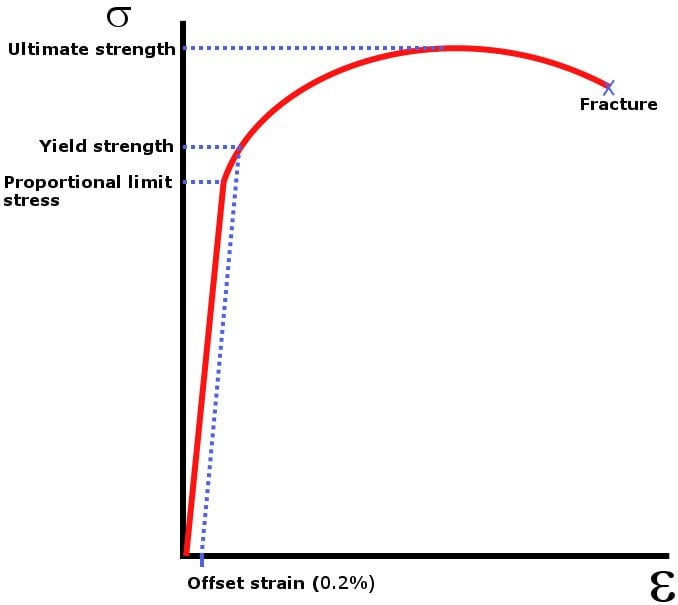


What Is Ultimate Tensile Strength Science Abc



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



Material Science


Strength Density



What Is Yield Strength Of Any Material Hindi Urdu Yield Strength क य ह Youtube
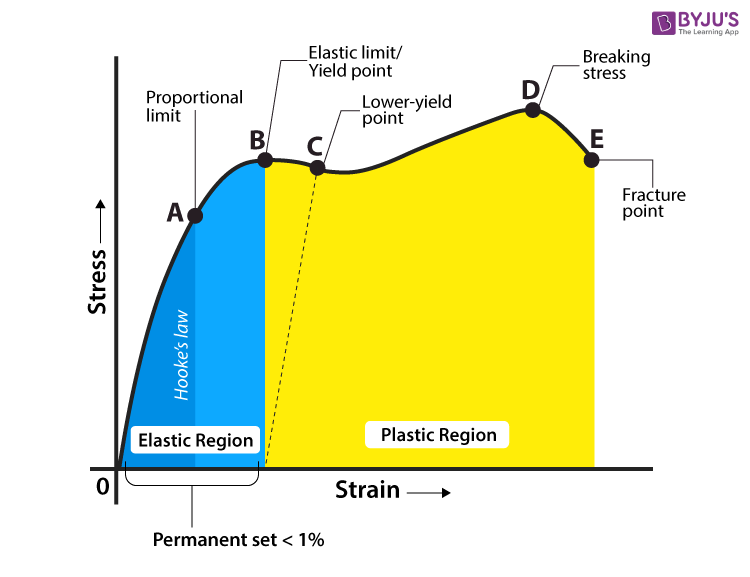


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
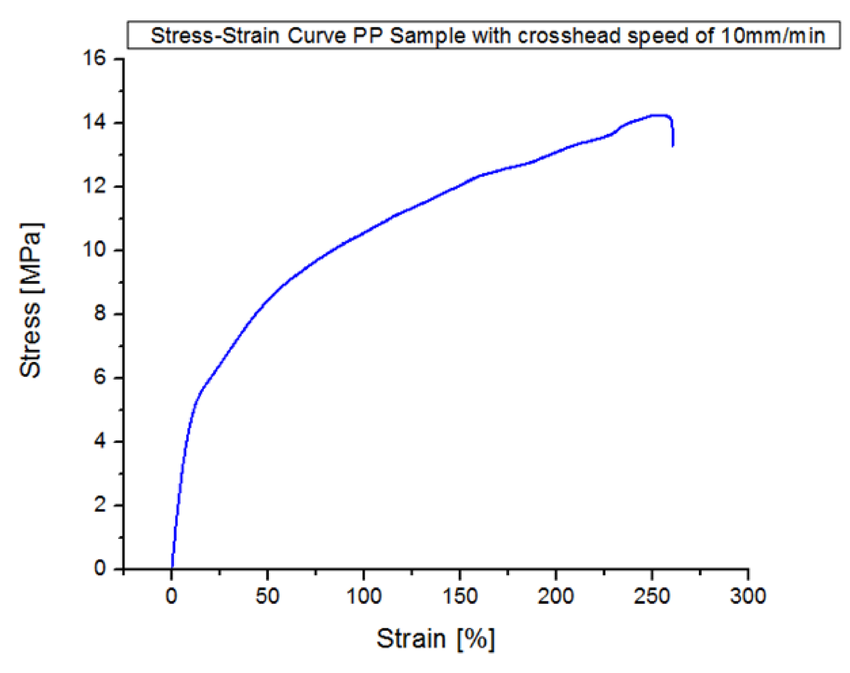


113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic



Yield Strength Metallurgy For Dummies


Q Tbn And9gctox3cf4zpt H1tpvycayerw3xbv Ukqszfzrag5mxfqpo7il42 Usqp Cau



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
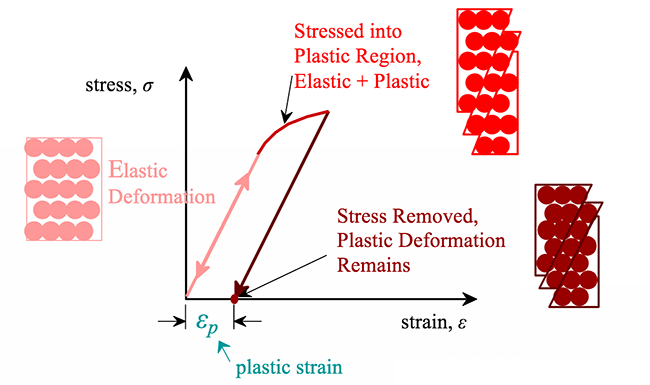


Plastic Deformation Matse 81 Materials In Today S World



Ultimate Tensile Strength Importance Testing Examples Fractory
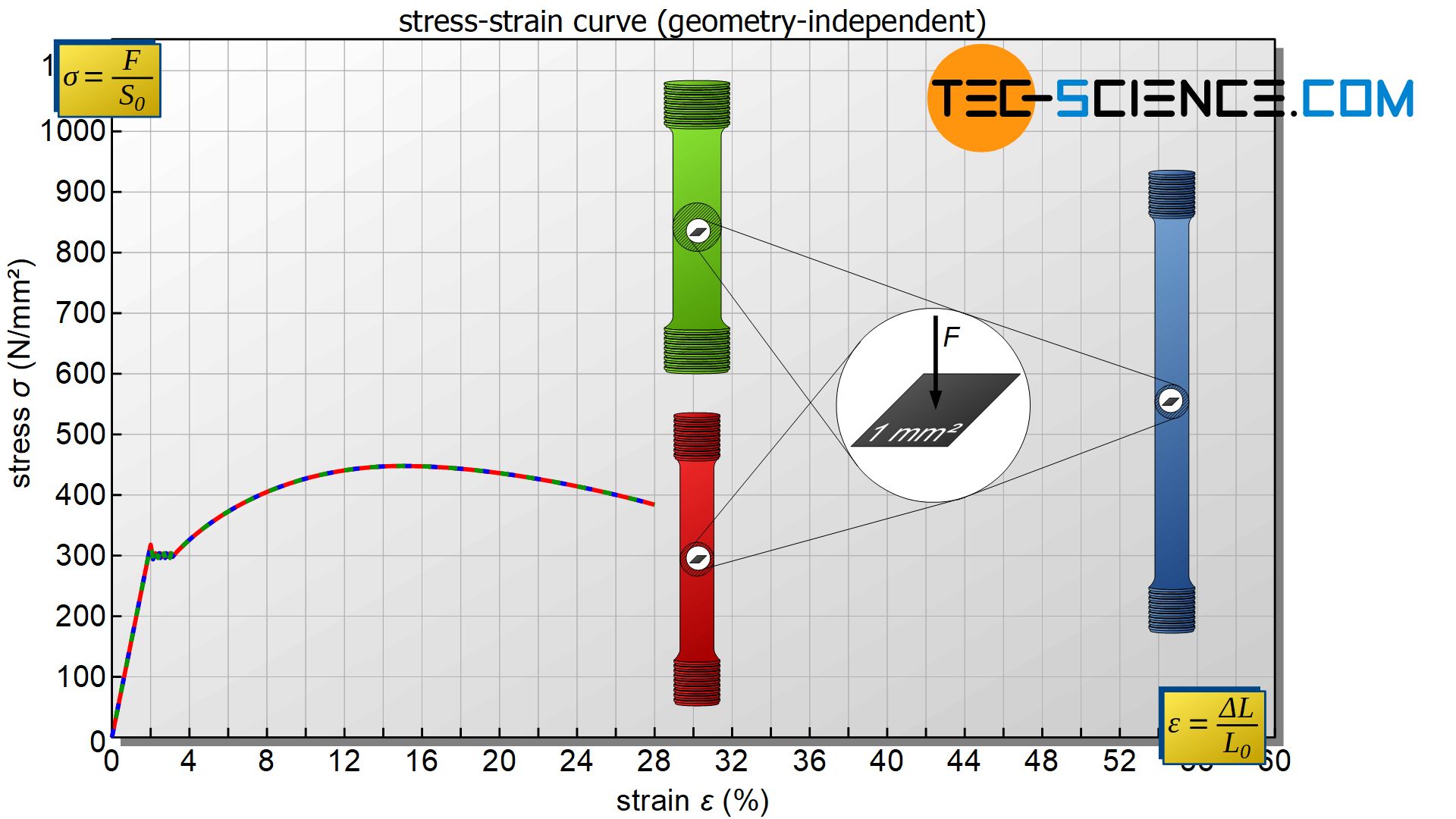


Gvvy2hhnalj6dm
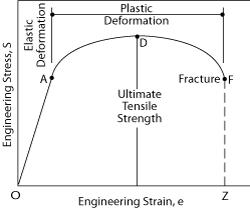


Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets
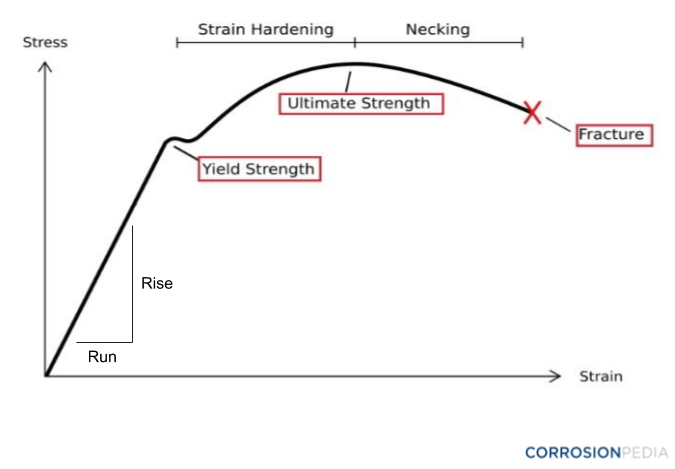


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia



Materials Science



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
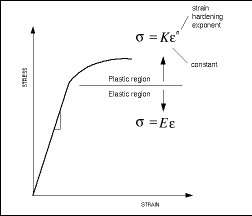


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal


Q Tbn And9gcq Lokv6u6biweu7e6sd5mb7neolnaw Dcdbogfctf 8hvcdutp Usqp Cau


Mechanical Properties Of Dental Materials



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora



Mechanical Properties Of Engineering Materials Electrical4u


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness



Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets



What Is Tensile Strength What Does Tensile Strength Mean Tensile Strength Meaning Explanation Youtube
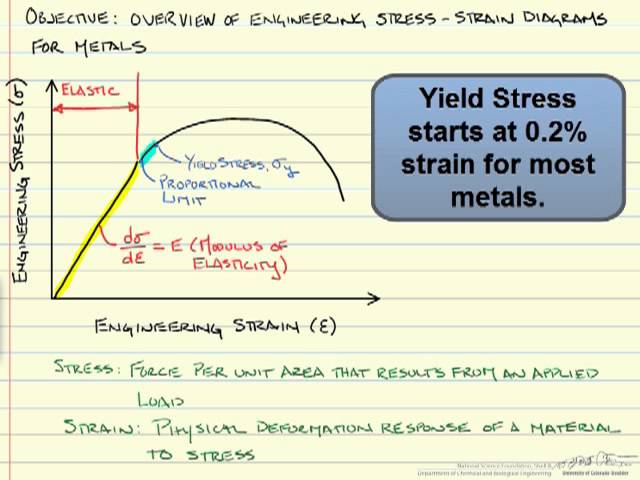


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube
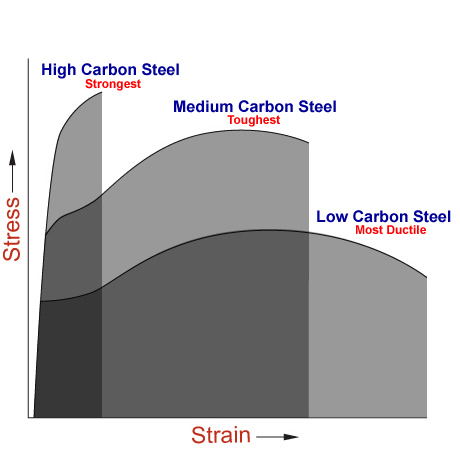


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora



High Tensile Steel An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


What Is The Difference Between Tensile And Yield Strength Quora


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf



Tensile Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
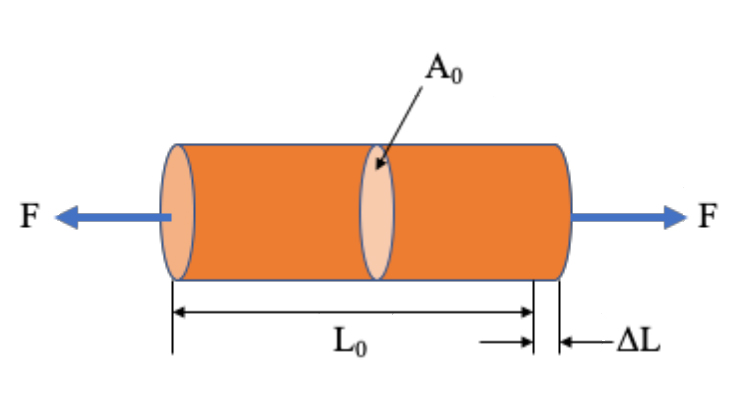


Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Materials Science
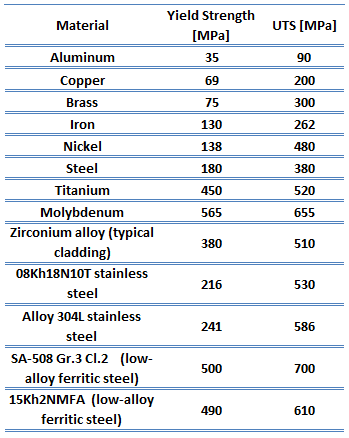


What Is Stress Strain Curve Stress Strain Diagram Definition Material Properties



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Strength Of Materials Wikipedia



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations


Q Tbn And9gctk9iq8odyr8oad6ztec3f7a2cfwevlxhbui8zaefsdyzdh0s1n Usqp Cau


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I


コメント
コメントを投稿